UAE E-Invoicing: Not Only a Tax Obligation but a Finance and Governance Transformation
UAE e-invoicing is not only a tax obligation. Learn how finance, AR/AP redesign, data governance, and controls determine compliant, audit-ready invoicing.
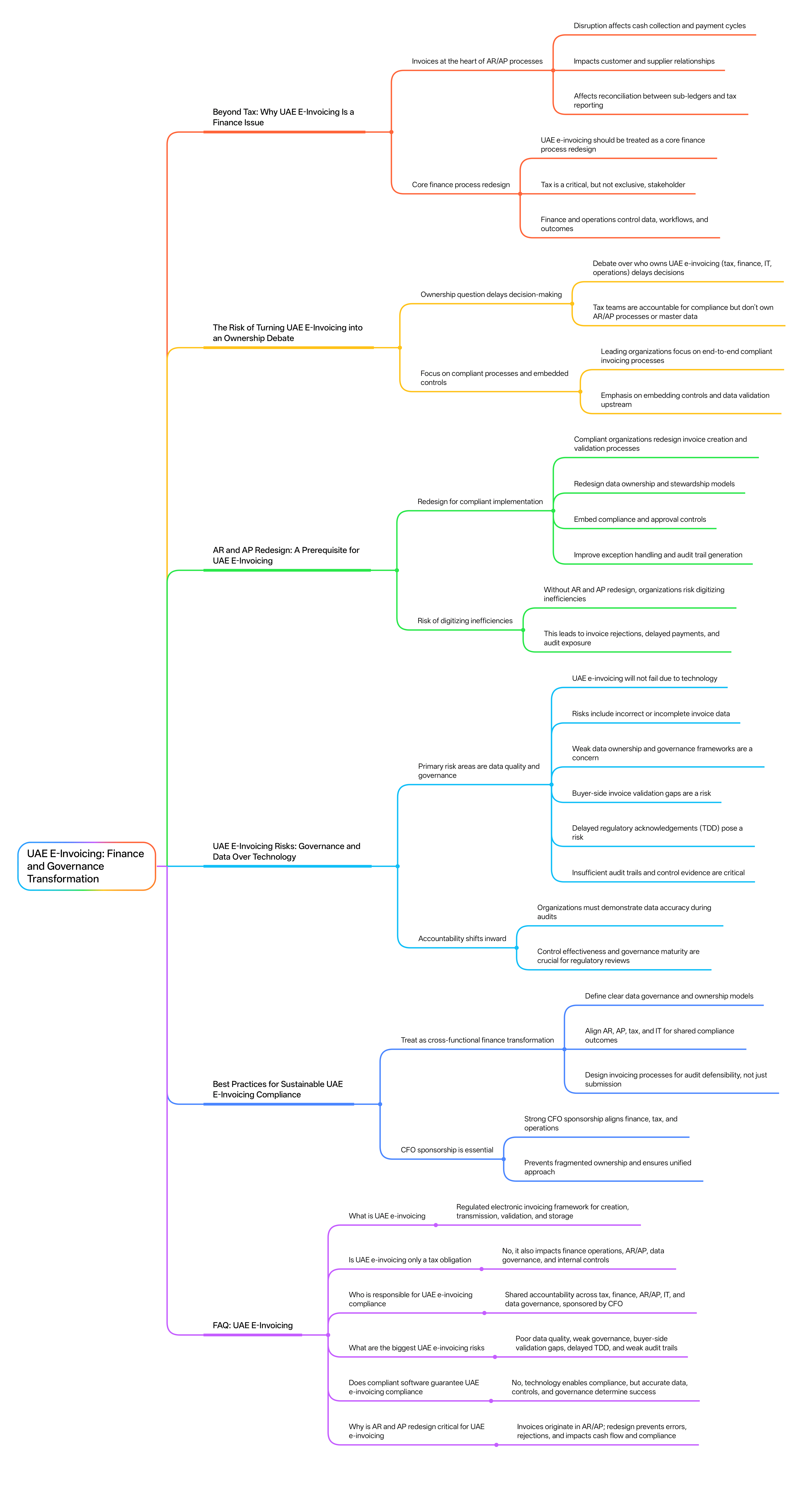
UAE e-invoicing is frequently described as a tax obligation. While this is correct from a regulatory perspective, it is an incomplete framing. In practice, UAE e-invoicing is not only a tax requirement, but also a finance operations, data governance, and internal control transformation that directly affects revenue flows, working capital, and audit defensibility.
Organizations that approach UAE e-invoicing solely through a tax lens often underestimate the scale of organizational change required and overestimate the ability of technology alone to deliver sustainable compliance.
Beyond Tax: Why UAE E-Invoicing Is a Finance Issue
Invoices sit at the heart of Accounts Receivable (AR) and Accounts Payable (AP) processes. Any disruption or inefficiency in invoice creation, validation, transmission, or acceptance immediately affects:
- Cash collection and payment cycles
- Customer and supplier relationships
- Reconciliation between sub-ledgers and tax reporting
From an advisory perspective, UAE electronic invoicing should be treated as a core finance process redesign, with tax as a critical—but not exclusive—stakeholder.
This distinction matters. While tax teams focus on regulatory alignment, finance and operations teams control the data, workflows, and outcomes that determine whether UAE e-invoicing works in practice.
The Risk of Turning UAE E-Invoicing into an Ownership Debate
A recurring challenge in UAE e-invoicing programs is the tendency to frame implementation as an ownership question:
Is UAE e-invoicing owned by tax, finance, IT, or operations?
This debate delays decision-making and reinforces silos. In reality, tax teams are accountable for compliance outcomes, but they typically do not own AR/AP processes, customer master data, or procurement workflows.
Leading organizations reframe the discussion and focus instead on:
- What invoicing processes must operate compliantly end-to-end
- How controls and data validation are embedded upstream
This mindset shift is critical for scalable UAE e-invoicing compliance.
AR and AP Redesign: A Prerequisite for UAE E-Invoicing
UAE e-invoicing cannot be implemented successfully as a bolt-on solution. Advisory experience consistently shows that compliant organizations redesign:
- Invoice creation and validation processes
- Data ownership and stewardship models
- Embedded compliance and approval controls
- Exception handling and audit trail generation
Without AR and AP redesign, organizations risk digitizing inefficiencies, leading to invoice rejections, delayed payments, and audit exposure.
UAE E-Invoicing Risks: Governance and Data Over Technology
In the UAE context, the risk profile is clear: UAE e-invoicing will not fail because of technology. Most organizations can implement technically compliant platforms.
The primary risk areas relate to data quality and governance, including:
- Incorrect or incomplete invoice data
- Weak data ownership and governance frameworks
- Buyer-side invoice validation gaps
- Delayed regulatory acknowledgements (TDD)
- Insufficient audit trails and control evidence
UAE e-invoicing shifts accountability inward. Organizations must be able to demonstrate data accuracy, control effectiveness, and governance maturity during audits and regulatory reviews.
Best Practices for Sustainable UAE E-Invoicing Compliance
To achieve long-term compliance and operational efficiency, organizations should:
- Treat UAE e-invoicing as a cross-functional finance transformation
- Define clear data governance and ownership models
- Align AR, AP, tax, and IT around shared compliance outcomes
- Design invoicing processes for audit defensibility, not just submission
Strong CFO sponsorship is essential to align finance, tax, and operations and prevent fragmented ownership.
FAQ: UAE E-Invoicing
What is UAE e-invoicing?
UAE e-invoicing is a regulated electronic invoicing framework requiring compliant invoice creation, transmission, validation, and audit-ready storage.
Is UAE e-invoicing only a tax obligation?
No. UAE e-invoicing also impacts finance operations, AR/AP processes, data governance, and internal controls.
Who is responsible for UAE e-invoicing compliance?
Compliance requires shared accountability across tax, finance, AR/AP, IT, and data governance teams, typically sponsored by the CFO.
What are the biggest UAE e-invoicing risks?
The biggest risks are poor data quality, weak governance, buyer-side validation gaps, delayed acknowledgements (TDD), and weak audit trails.
Does compliant software guarantee UAE e-invoicing compliance?
No. Technology enables compliance, but accurate data, embedded controls, and mature governance determine success.
Why is AR and AP redesign critical for UAE e-invoicing?
Because invoices originate and are processed in AR and AP. Without redesign, errors and rejections increase, impacting cash flow and compliance.

Monish Mohan is a versatile and accomplished Auditor, VAT Consultant, Finance and Accounts Professional offering over 18 years of experience in UAE VAT, Audit & Assurance, Finance management Advisory & Accounting & bookkeeping.







